Editorial strategy in a nutshell
By Creative team. Top image: Leonardo AI.
Your quick guide to creating content that drives results
The purpose of an editorial strategy is to ensure that all content produced:
Delivers on your business objectives
Is aligned to your brand positioning
Resonates with your target audience
The strategy serves as a roadmap that enables you to consistently create, produce, and distribute brilliant content to the right audience, in the right channel, at every stage of the customer journey.
By mapping your strategy to your resources and KPIs, you can also streamline production, organize workflows, prioritize your efforts, and optimize your results.
Ultimately, an editorial strategy transforms content creation from a reactive, ad-hoc process into a purposeful and cohesive effort, enabling brands to communicate effectively, stand out in competitive markets, and adapt to evolving audience preferences.
Here are the key elements of editorial strategy…
1. Define your objectives
Establish clear, measurable objectives for your strategy that align with your brand’s overall goals. Your objectives determine the type of content you produce and how success will be measured.
Examples of objectives:
Increase brand awareness
Drive conversions
Generate leads
Customer retention
Educate and engage your audience
Position the brand as an industry thought-leader
Strengthen the brand’s cultural relevance
2. Map your audience
Content only works if it connects. So understanding your audience’s demographics, behaviors, pain points, needs, values and interests is mission critical.
Steps to understanding your audience:
Ingest all available audience research and conduct additional studies as required. (Include psychographics, ethnographics, focus groups, social listening, analytics, demographics etc).
Identify your most important audience segments e.g. the most profitable, largest, most influential etc.
Drill down into their characteristics and preferences.
Understand their customer journey and how to reach them (content types, platforms, tone).
3. Clarify your brand proposition
Articulate what your brand stands for and how it adds value to your audience.
Define your unique value proposition (UVP). What’s your why? What’s the key problem your brand solves?
Pinpoint your brand’s position in the market.
That enables you to clarify your brand voice and tone (formal, conversational, authoritative, rebellious, disruptive).
Communicate or establish additional brand guidelines to ensure all content is consistent and aligned with your brand’s purpose, position, and values.
4. Conduct content research and audit
Analyze your existing content to identify what works and where the gaps are.
Content audit: Evaluate your website, social media, videos, ads, and other assets. What do you have? What needs to be updated, improved, or replaced?
Competitive analysis: Understand what competitors are creating and identify opportunities to differentiate.
Gap analysis: Highlights missing content for specific audience needs or journey stages.
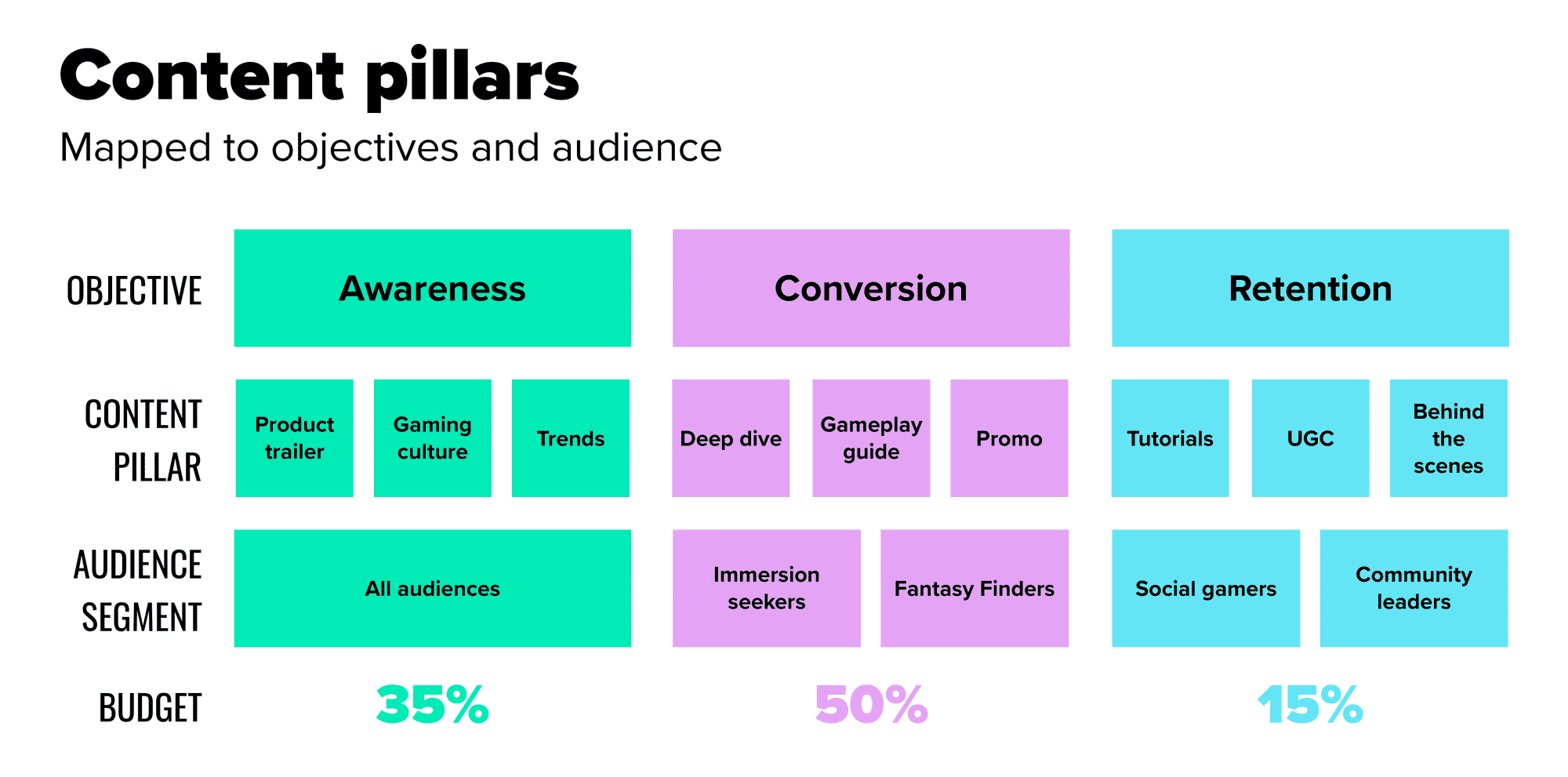
5. Establish your core content pillars
Core content themes sit at the intersection of your objectives, brand proposition, and the audience’s interests. These pillars maintain focus and prevent producing content that is off-brand or irrelevant.
Content pillar examples for a videogame brand:
Tutorials and gameplay guides.
Deep dives into game mechanics, levels, lore and characters.
Behind-the-scenes looks at feature development.
Developer diaries explaining creative decisions.
UGC and community engagement stories.
Gaming culture and trends content.
Shareable entertainment and humor centered on gaming life.
Product news, announcements, and promos
By aligning your pillars with your objectives and audiences, you can decide how much of your time and budget to allocate to each theme.
6. Select the right content and channels
With the pillars established, we need to decide what type of content to produce, in which format, and where to distribute for maximum ROI:
Content formats include:
Educational, tutorial, walkthrough
Q&A and AMA
News and announcements
Promos and giveaways
Trailers and teasers
Interviews, reactions, and insights
Behind-the-scenes
Retrospectives and nostalgia
Competitions, quizzes, challenges, tournaments and co-op projects
Community spotlights
Case studies
Content types include:
Videos, webinars, podcasts, live stream
Blog posts, newsletters, whitepapers
Photos, screenshots, infographics, illustration
Live events - IRL and virtual
Channels:
Owned media (website, blog, email)
Earned media (press, influencer mentions)
Paid media (ads, sponsored posts)
Shared media (social platforms)
Different formats and content types appeal to different segments of the audience and serve various purposes.
Naturally, the channel blend is optimized to maximise reach and impact.
Smart planning ensures assets are used cross-channel to maximise production efficiency. It’s important to create content so it can be rapidly recut and adapted to native platform behaviors.
7. Create a content calendar
A well-organized content calendar facilitates a steady flow of relevant and timely content:
Organize content ideas and campaigns by pillar, format, and channel.
Schedule content across weeks and months while leaving room to react to events, trends, and news.
Ensure your deadlines allow time for stakeholder feedback and approvals.
8. Assign roles and responsibilities
Clear processes for content creation, review and approval ensure accountability, maintain quality, and streamline production. Defined roles, responsibilities and workflows improve efficiency and keep content aligned with the strategic vision.
Key roles can include:
Content strategist: Oversees the strategy and calendar.
Content partners, writers, designers: Create the content.
Editors: Ensure quality, brand voice, and accuracy.
SEO specialist: Optimize content for search engines.
Analyst: Measure content performance.
Project management tools offer an invaluable assist when managing workflows.
9. Implement SEO and data-driven practices
Ensure your content is discoverable and optimized for search and audience preferences.
Conduct keyword research for relevant topics and search intent.
Ensure you implement native SEO best practices for every platform including social media and AI search.
Deploy SEO tools and train all creators to optimize their content for discoverability.
Monitor what’s working for your competitors and conduct regular content gap analysis.
Monitor key metrics and update content to improve rankings.
Keep your SEO practices up-to-date with changes in the algorithms.
10. Measure performance and optimize
Track effectiveness using agreed KPIs to measure what’s working and where improvements are needed.
Common KPIs:
Traffic (organic, referral, paid)
Engagement (shares, comments, dwell time)
Conversions (leads, downloads, sales)
Brand awareness (brand mentions, consumer sentiment scores)
Naturally, continuous analysis and optimization are essential to refining the strategy over time.
The role of generative AI
AI is an essential productivity multiplier at almost every stage of the editorial process. It isn’t currently good enough to automate any element, but access to the right AI tools (and training for every member of the team) is rewarded by valuable efficiency gains.
Final thought: iterate and evolve
A successful editorial strategy is never static - it must continuously adapt to changes in audience behavior, industry trends, tech advances, and business objectives. Regular content audits and performance reviews will also help keep your strategy fresh and impactful.
But the most important discipline of all is to never allow your strategy to drift away from the twin poles of clear objectives and measurable results.
So long as every aspect is aligned to those critical navigation points then your content will deliver.
If you would like to discover more about our integrated approach and work together on a project, get in touch.